Written by Rocío Rodríguez
Índice
What is Google News?
Google News is a Google platform that stores a large number of news and articles about recent and current events. We can find from large and authoritative media such as El País or As to others that have a lower traffic weight and popularity. Any news website is eligible to appear in News, as long as it complies with the established inclusion requirements.
The main objective of this platform is to organize the news, to offer an optimal information experience, making available to the reader valuable content and useful news that are of interest to them.
How do I include my website as a Google News source?
To request inclusion, all we need to do is send a request from the Google News Publisher Center. Google will proceed to perform a manual review of the site to verify whether or not it complies with the stipulated quality requirements. However, submitting a news portal through the Publisher Center does not ensure inclusion of the website as a Google News source.
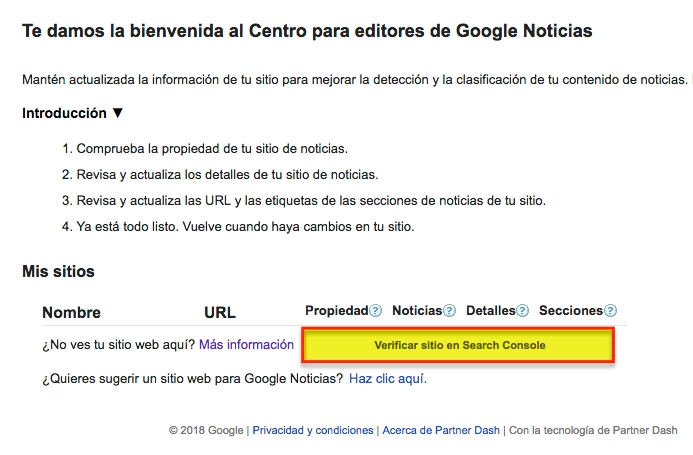
First of all you must verify in Search Console that you are the owner of the website you want to register in the Publisher Center.
Next, you will need to log in to the Publisher Center with the same email account you used to verify ownership of your news source in Google Search Console.
Once this is done, we will be able to request the inclusion of our site in Google News from the Publisher Center, for which it will be necessary to include information about the portal such as the URL and the tags of the news section. As a general rule, the process of submitting and including a portal as a Google news source usually takes approximately one to two weeks. To check if Google accepts our request we will have to access the Publisher Center and check the status, which at first will appear as “Under Review” or similar. This status will change to “Included” if our news source meets Google’s quality guidelines.
Requirements for the inclusion of a web site in Google News
We recommend that before submitting your site to Google News you review Google’s technical and general guidelines because if you do not meet the specified requirements, Google will deny our request and we will not be able to reapply for inclusion for 60 days.
Technical guidelines
Accessible and indexable content
We must not block the crawling and indexing of any of the sections or pages submitted to Google News through the robot.txt or through the robots meta tag of the site. Crawlers must be able to access all these URLs if they are to be included in News.
Format of articles
The news must be in HTML format. GoogleBot cannot parse PDF files.
HTML links
The format of the links must be the usual one, that is to say, we will avoid links that are not HTML such as JavaScript, graphic links or links included in frames. Although Google is getting better and better at interpreting and executing these types of links, we recommend that you continue to use HTML links. The syntax of an HTML link would be as follows:
<a href=”http://www.midominio.com/”>Home of Midominio.com</a>
General guidelines
Writes current news
It is very important to differentiate between articles and promotional content such as advertorials, and current news. If your web portal makes available to the user different types of content, I advise you to submit to Google News only the sections that offer information on recent events. We will avoid, therefore, the sending of:
- How-to articles
- Advice columns
- Job offers
- Real estate ads
- Strictly informative content
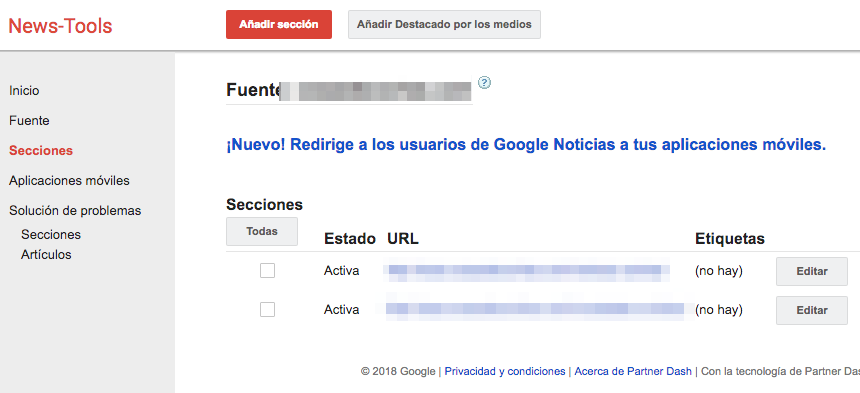
From the Editors Center you can select the sections you are interested in sending to Google News. In this way you will be able to discard the sections of the website that include content of a different nature to that required. All you have to do is access the “Sections” section of the Publisher Center and include the URLs to be sent. For example, if we are a web portal for renting and selling apartments online and we have a section on the site where current news about the real estate sector is published, we should only inform Google to take into account the content of this section and not the rest.
Date and author of content
Google News only includes news published in the last two days, so it is important that the search engine can correctly track the date of publication of the article.
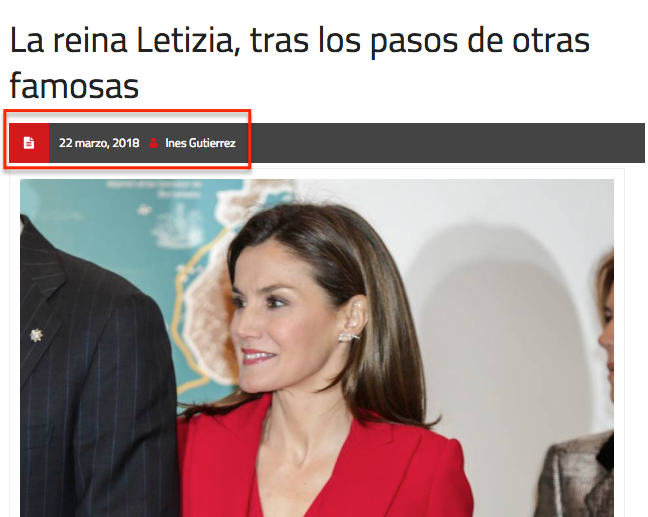
We recommend placing this information in a visible section of the page, for example, at the top of the news item, as Love Magazine does:
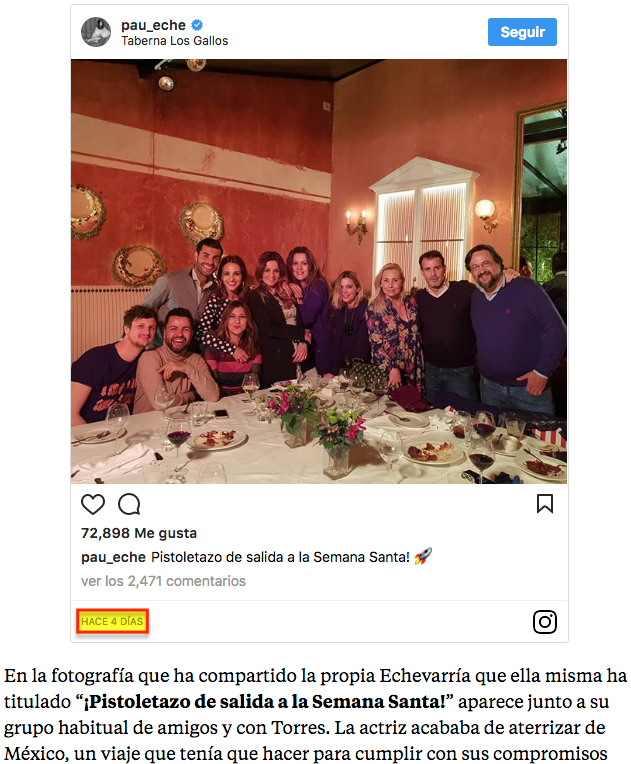
This point is important because we have found cases in which the spiders were taking as the publication date of the article other dates included in the news and that were far from the actual publication date, such as, for example, dates of excerpts from Tweets, Instagram photos or even the dates of the news update.
The image attached below shows an embedded image from Instagram displayed in an article from a heart magazine and containing a date that Google could take as primary if we do not locate the actual publication date of the news item in a visible place on the page that GoogleBot can crawl.
Although in the news sitemap we incorporate the tag <publication_date>, inserting the date and time in the article is also necessary to appear in Google News.
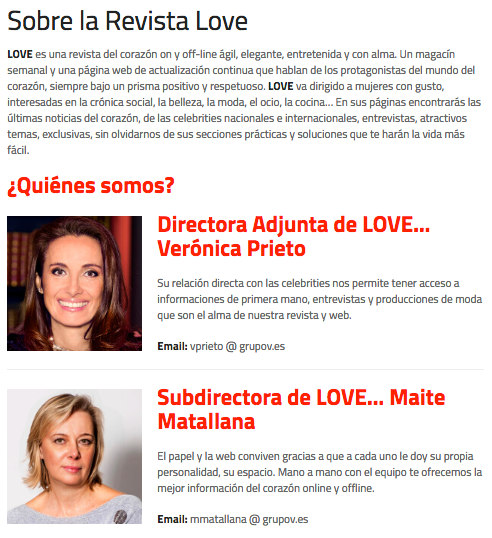
Information on the environment
It is recommended that the website include a page with a brief description of the site, the biography of the editors and managers of the portal and a photograph of each of them. One way to implement this could be as they do at Love Magazine:
 Contact information
Contact information
It is recommended that there be a page on the website that lists contact information such as physical addresses, telephone numbers or e-mail addresses, as well as as as much organizational and liability information as possible.
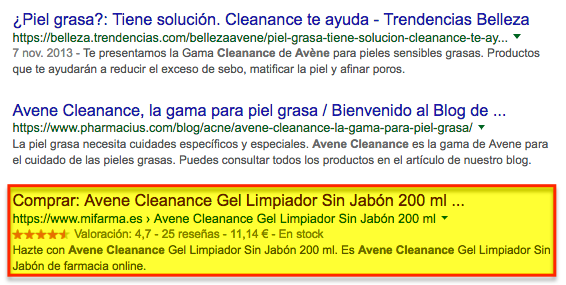
Any information that may be offered will be evaluated to detect the level of credibility of the media. An example could be the contact page of El País:
Advertising
Advertisements or any other type of promotional material used must not exceed the main content of the page.
Pages in AMP format
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) is an open source initiative promoted by Google together with a large number of media worldwide and other technology partners. AMP was created with the aim of improving the loading speed of mobile web pages. Validated AMP pages are stored in Google’s AMP cache, which allows them to be published even faster.
If our pages do not have an AMP version, we will have no chance of appearing in Google’s horizontal carousel for searches performed from mobile devices. In addition, we will lose positioning possibilities for searches performed from these devices because Google will favor AMP pages, which have a slower loading speed, in its ranking. This is due to the fact that they contain less code because they do not contain elements such as sidebars, related contents, etc.
In this article we take a closer look at AMP pages.
Google recently announced AMP Stories, a type of content in audiovisual format that is integrated into Google.es and designed for the media. It mimics the already familiar Snapchat, Instagram Stories and Facebook stories. The objective of this new initiative is to offer users news in AMP format but making use of visual and rich content. There is still not much information about this new result format but if you manage an online media you should take it into account.
Google may deny the inclusion of a website if it does not meet any of these technical and general requirements mentioned above. Likewise, it can also cease the activity in News of a portal already included if it does not respect or violates any of the required quality guidelines, as well as if it shows prohibitive behaviors or misleading practices.
Other recommendations
Unlike the guidelines listed above (general and technical), the recommendations in this section are not mandatory. Similarly, at Human Level we do recommend its implementation.
Structured data
Your website may be approved as a Google News source whether or not it has structured data markup. However, it is worth considering its implementation as structured data helps Google understand the content of a website by providing it with additional information.
Structured data markup is implemented in the source code of the page and its function is to describe the web content as well as its properties. For example, if a site has recipes, bookmarks can be used to describe the ingredients of the recipe, the image of the dish, the rating of the users, etc.
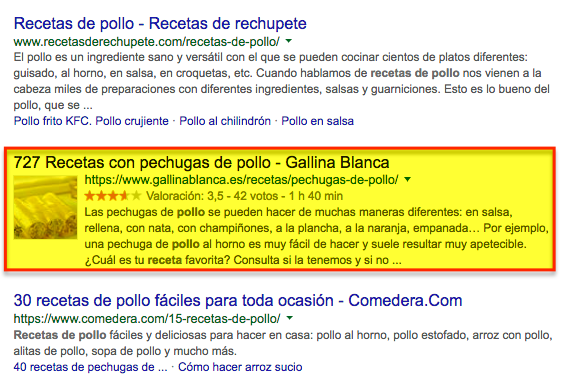
This allows Google to better understand the site’s content, which can help it to be indexed more effectively, in turn allowing results to be more relevant to users’ searches.
As we have seen in the two previous images, the data markup is displayed to the user in the form of rich snippets. These make the result much more attractive and therefore more likely to be clicked than a normal result. When we talk about rich snippets, we refer to the featured information that appears below each search result, such as a user rating, the price of a product, the preparation time of a recipe, the time and place of a concert, etc.
Although the inclusion of structured data does not influence the positioning of the site, that is, its inclusion will not cause our results to rank in more privileged positions, it can help to improve the CTR of the page.The chances of a user clicking on a rich result will increase. Google currently displays rich snippets for products, recipes, events, reviews, apps, videos and articles.
This is additional information that complements the information already displayed in a normal result and makes it a more prominent result.
We list below the types of structured data markup that can be implemented in news portals:
- NewsArticle and Article data tagging
This is, along with Article’s structured data, one of the main markers for online media. It is used to mark the main content of the page.
In the case of news portals, it is recommended to implement the microformats“Article” for articles and“News article” for news. News are all those current publications that, unlike articles, do have a temporary nature.
Google’s “Structured Data Testing Tool” can be used to test the correct implementation of microformats.
- Author data marking
This data marking allows to indicate the authorship of the news item. It is not as fundamental as the previous one, but we do recommend its inclusion whenever it is possible to implement it.
- Data Marking Date Published
Through this markup we can indicate to Google the date of publication of the article. This makes it easier for crawlers to understand how old the item is. Remember that Google News only includes publications that are no more than 24 hours old from the date of publication, so this type of marking also plays a significant role and should be taken into account as one of the optimizations to be made if you are going to request the inclusion of your portal in News.
There are also other structured data with a lower level of importance that we can also consider when making the implementation such as the one that allows us to mark the comments made by users.
Google News Sitemap
The function of the Google News sitemap is the same as that of the sitemaps of web pages or images. The main objective is to facilitate the process of locating the site’s news URLs. If Google discovers more quickly the news articles that we publish on our site, we will have a higher probability of appearing in Google News than another media that has published a piece on the same topic but has not submitted it in the sitemap, since it will be more difficult for Google to reach it. Although the sitemap file does not ensure that the news included in it will be indexed, it allows us to leave a series of “breadcrumbs” that will help crawlers to reach the news more easily.
We should avoid submitting the news sitemap before the site has been reviewed and included in News, as this may result in errors.
Google does not favor websites that have a news sitemap. However, it is advisable to have this file so that crawlers can reach pages that they would not be able to access through the usual crawling mechanisms.
Although the objective and functionality of the news sitemap is the same as that of the web page and image sitemaps, the former has a series of specific guidelines that must be followed if we want this file not to register any type of error and to be processed correctly.
Includes the URLs of articles published in the last 2 days.
News that are more than two days old, counting from the date of publication, should not be included.
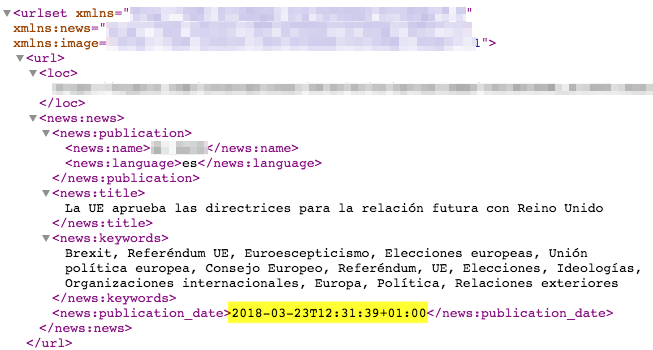
In the image attached below we can see an excerpt of a media sitemap from March 20, 2018. As can be seen, the first two news items included have the same publication date of March 20, which is correct.
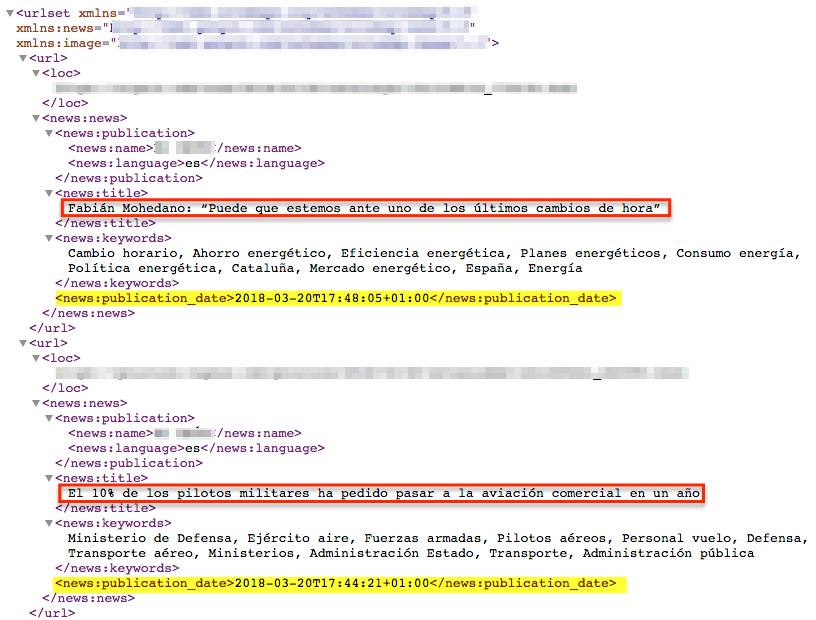
Sitemap update
We recommend updating the News sitemap as new articles are published, in this way we will make available to Google the latest news in order to crawl and index them to be able to return them as results in Google News for related searches.
Maximum number of URLs
We should not add more than 1000 URLs. This is the figure that Google stipulates as the maximum allowed. If your website is large and you want to add more URLs, you should split them into several sitemaps and use a sitemap index file to manage them. This limitation is set in order to ensure that the server is not publishing large files on Google News.
Specifies the correct labels
We must pay attention to the tags of the news sitemaps that Google indicates as mandatory:
- The tag <publication> has, in turn, two subtags that must also be included: <name> and <language>
- The label <name> refers to the name of the news source. For example, in the case of El País, the name chosen could be “EL PAÍS”, in capital letters, or “El País”. Let’s imagine that the name of the source we finally select is “El País”, because this is how it should also appear in the vertical search engine of Google News and in the carousel of Google.es for relevant searches. As far as source name selection is concerned, there are no restrictions whatsoever. The only thing to keep in mind is that the name chosen must match the name that appears in the articles on news.google.com.
- The label <language> indicates the language of the publication. To represent it, it uses a 2- or 3-letter ISO 639 language code.
- <publication_date> indicates the date and time your article was published on the website. The publication date of the article must be specified in W3C format, with full date format (YYYYY-MM-DD) or full date format plus hours, minutes and seconds along with the time zone code (YYYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssCZH).
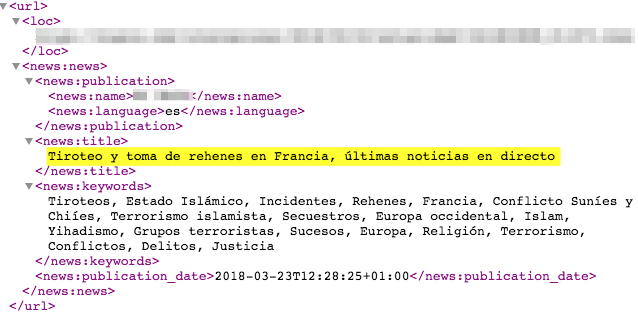
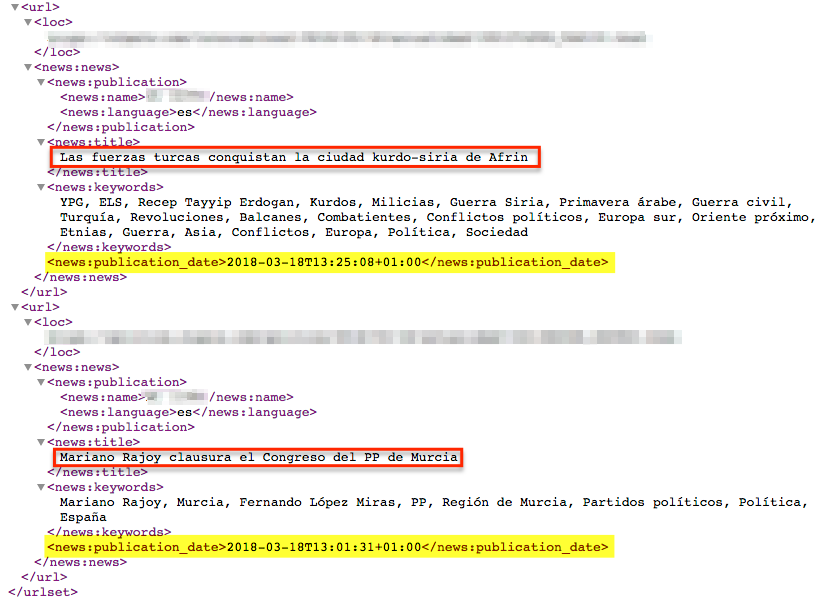
Below is an excerpt from a media sitemap in which the time is given using the full date format plus the hour, minutes, seconds and time zone code:
- <title>. In this tag we must indicate the title of the news item as it appears on your web site.
- <news_keyword>
Google uses this tag to rank the news in its index. We do not recommend including more than 8 keywords . The keywords included should be directly related to the event in question.
The order of inclusion of these terms does not give greater relevance to some over others.
Where does Google show the news?
We can access the news included in Google News from any device: smartphones, tablets, etc., desktop computers… Let’s take a look at it below:
Mobile
- Google.es vertical search engine
This section of the SERP includes a selection of the most recent news about the event that the user is consulting.
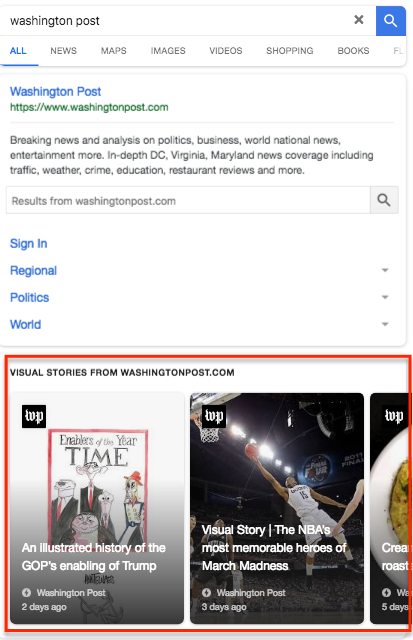
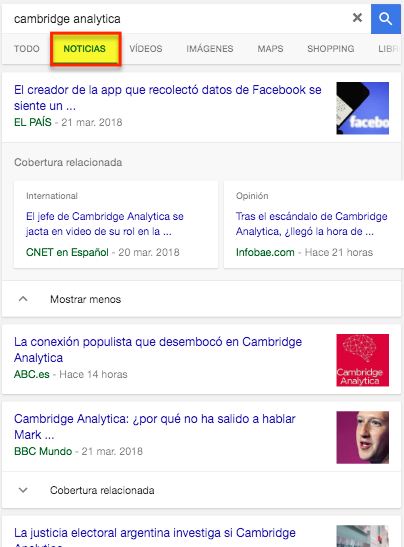
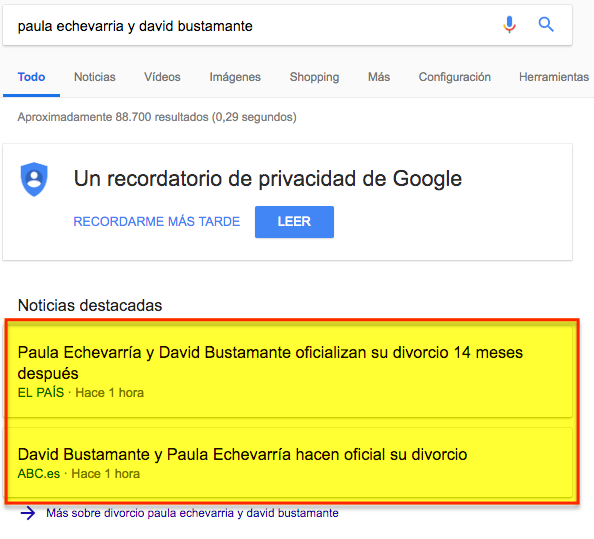
- Carousel of news highlights
A maximum of ten news items can appear in this block of the SERP and all the results that appear are directly related to the search query made by the user.
This type of results are more visually appealing than the conventional ones and appear above the organic results.
Normally, on mobile devices, we usually find this carousel accompanied by two links (located at the top) that lead to news related to the event in question:
However, these news items can be confused with conventional results, as they do not present any visual elements to help attract the user’s attention.
In the case of the image above, for example, there is a higher probability that the user will end up clicking on some of the news in the carousel before clicking on some of the two links at the top of the SERP.
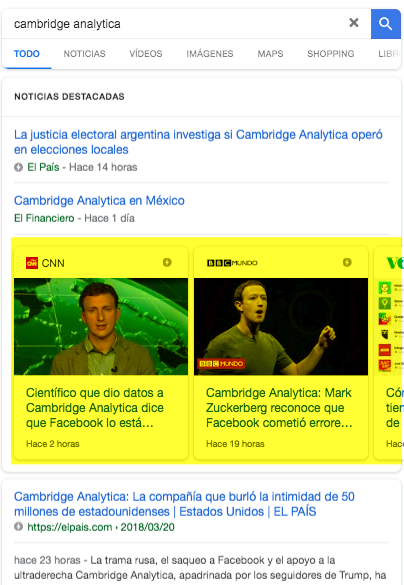
In addition to the carousel that appears in the “Featured News” section and is displayed after an organic search, there are other similar results of recent creation that combine characteristics of the conventional result along with others that are more typical of the carousel:
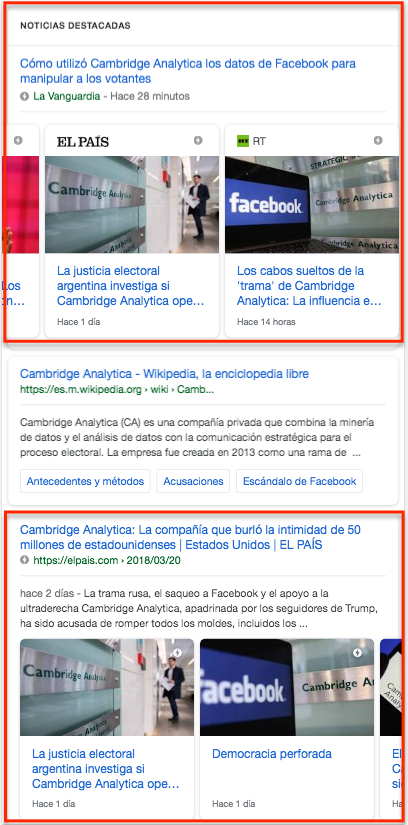
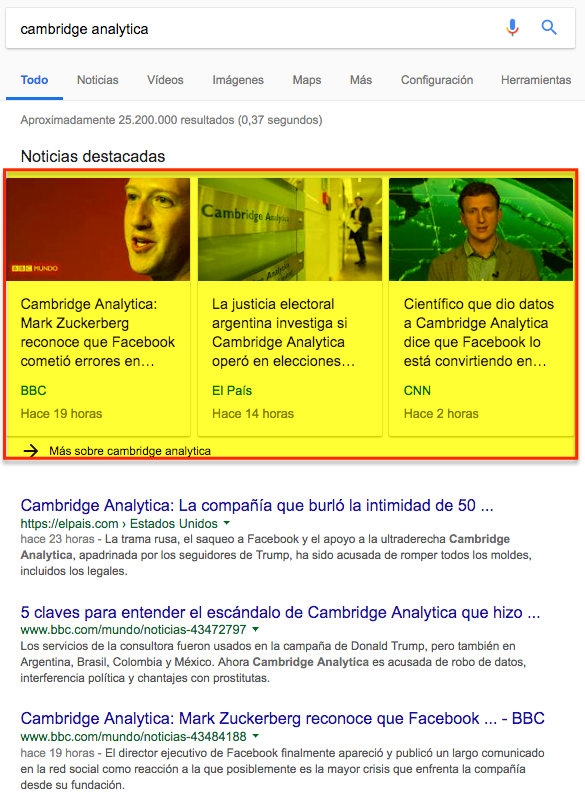
Organic results obtained after searching for “cambridge analytica” on Google.com using a mobile device.
In the case of the third result, we see that the title and excerpt of a specific news item is presented and next to it a series of highlighted news items are listed in carousel mode. These news items belong to the same media and, as we can see, they are related to the event or occurrence consulted.
We emphasize once again the importance of implementing the AMP format in your site pages if you want them to be displayed in Google carousels, both in the top block of featured news and in the results mentioned in this section of the article.
Desktop
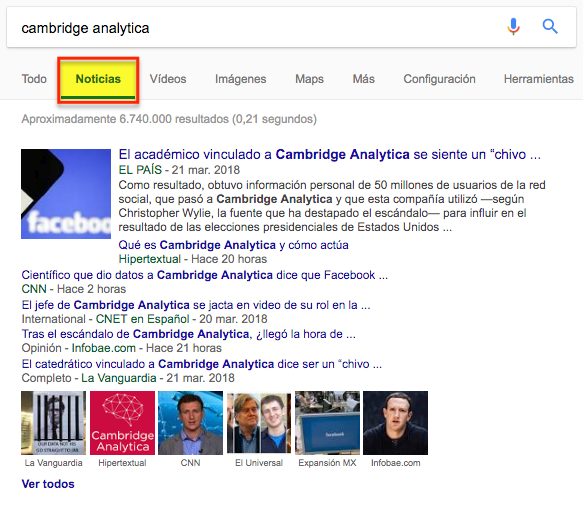
- Google.es vertical search engine
The news items are listed in a format very similar to conventional results: the title, the Google News source, the date of publication and, sometimes, a brief descriptive text of the news item are displayed:
- Carousel of news highlights
At the moment, three news items always appear in this section of the SERP. Either way, the user can find more information about the event or occurrence by clicking on the link below the carousel after which he/she will be directed to the Google News home page:
- Block of News Highlights with results without graphical elements
In this case, the format is more similar to that of a conventional result, since no images or any other visual element is used. Either way, we are gaining visibility by appearing at the top of the page, above the natural results.
Google uses its usual algorithm to calculate the positions of the results of the carousel and the news displayed in the vertical search engine.
Of all the insertions listed above, in terms of visibility, the featured news carousel acquires greater relevance since it is the first thing the user sees when searching. The percentage of users who access the vertical search engine of Google News is infinitely smaller when compared to the number of users who will end up clicking on any of the results displayed in the carousel.
This carousel scrolls down the organic results showing only the media whose news pages have been adapted to AMP technology.
However, many media outlets request inclusion in Google News but fail to see a positive impact on the site’s organic traffic. This is because the news do not manage to appear in the Google carousel and sometimes not even on the first page of the vertical search engine. We must work on the SEO on and off page if we want to achieve an optimal ranking. We recommend consulting the following article in which a series of recommendations are given regarding the optimization of current affairs content.
As you can see, Google News is an almost essential element to use whether we are an online media or if we manage or have a web portal that has a news section. Undoubtedly, it is an option to consider if we want to achieve greater visibility of our content.
Have you already included your content in Google News or are you planning to do so? Before applying for inclusion, we recommend that you follow the recommendations described throughout the article to ensure that the process is completed successfully.
 Contact information
Contact information