Written by Anastasia Kurmakaeva
Index
What is a user interface or UI?
In the field of information technologies, User Interface (UI) is a visual medium that combines a series of controls and elements that allow a user to communicate and interact with an electronic device.The information is stored on a computer, cell phone or any other type of computer equipment, as well as on a software or website.
A good user interface should be simple to use, easy to understand and easy to learn.
Most common types of interfaces
Text Interfaces (TUI)
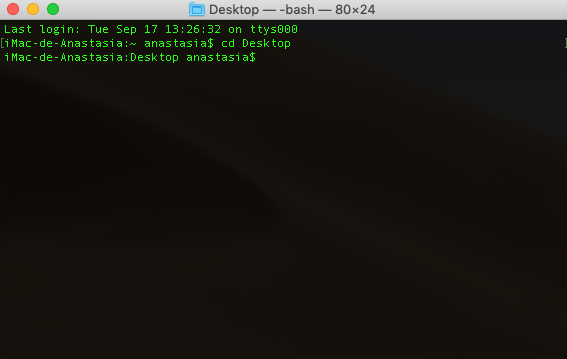
Text interfaces, as the name suggests, only display text and ASCII characters on a screen and are operated with the keyboard. It is practically limited to operating systems (nowadays in disuse) such as Norton Commander, MS DOS, Turbo Pascal… as well as BIOS management and configuration.
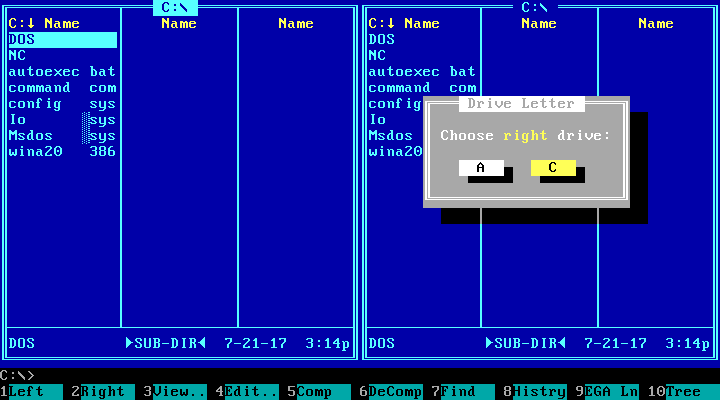
Command Line Interfaces (CLI)
It is probably the oldest type of interface still in use today. It consists of the user entering commands and instructions to the computer in writing and getting feedback based on the request. As it is a text interface, only ASCII characters are used for both input and output.
One of the major shortcomings of command line interfaces is that the user needs to know and memorize a wide variety of commands to be able to interact with the device in an agile way, which makes them too complex. Nevertheless, this method continues to be considerably relevant in the software development and system administration sector for certain tasks, such as version control using the Git system.
All major desktop operating systems have their command line applications: Terminal on MacOS and the Linux family, Command Prompt on Windows, Chrome Shell (CROSH) on Chrome OS…
Graphical User Interfaces (GUI)
Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) revolutionized the world and came to (almost) replace text and command line interfaces by greatly simplifying user interaction.
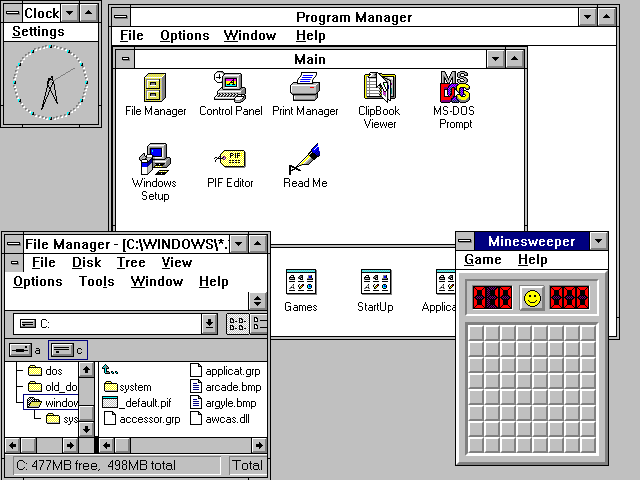
They are currently the most widely used type of interface. The software displayed on the screen is operated by means of the mouse or trackpad and the keyboard, as well as the various graphic elements of the interface: buttons, toolbars, menus, icons, windows…
GUIs are the type of platforms that today we also use on our mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, although these, in part, also belong to the category of natural user interfaces (NUI) – which we will see next – due to their tactile properties.
Natural User Interfaces (NUI)
Natural User Interfaces are the most friendly and intuitive type of interfaces, allowing a very fluid interaction based on gestures, voice and/or touch, all of these “natural” characteristics of a human being. They can have a physical support, but they can also be invisible to the user.
- NUIs can rest on touch screens, such as those in smartphones, but they can also exist outside of screens and rest on other surfaces, to still be operated by touch. They lead to a very natural and direct interaction.
- Another type of natural interface are those with gesture and motion recognition capabilities. A good example of this type are video game consoles, such as Nintendo Switch, which use special controllers, equipped with gyroscopes and accelerometers to detect gestures; or even cameras with motion sensors in the case of Sony PlayStation and its PlayStation Move accessories.
- Devices with voice recognition allow users to interact with them through voice commands. Their interfaces are able to identify words and expressions, which with a series of computations are transformed into a format that they can understand to provide the desired feedback based on user input. Examples implementing this type of interface include, once again, mobile devices and their hands-free functionalities, voice assistants, smart speakers such as Google Home, HomePod, Alexa, etc.