Written by Jose Vicente
Index
Google defines snippets as lines of text that appear below each search result and are intended to inform users about the content of the page and to show them why it is relevant to their query.
Advantages of enriched fragments
If Google understands the content of the pages, we can create rich snippets with detailed information to help with specific user queries. These rich snippets help users know if a site is relevant to their search by displaying more data than the simple description relevant to their search.
Google does not guarantee that rich snippets will be displayed and displaying this extra information in the SERPs will not improve rankings. Sohow do rich snippets increase SEO traffic, the answer is simple, by adding more visual impact to our results and giving more credibility to the information contained in the pages of our site. If we get the user to look first at our result and that it seems sufficiently relevant to their search, not being first loses importance.
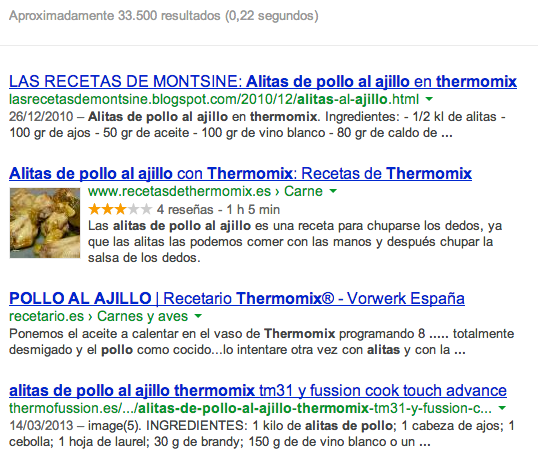
Let’s take as an example a recipe blog, for each of your recipes you can show an image, the users’ evaluation and the preparation time.
The effect of the use of this type of structured data has caused the following visual modifications:
- Image with the final result of the recipe that increases the credibility of the preparation.
- User ratings from 0 to 5 stars.
- Number of users who have voted for the recipe.
- Recipe preparation time.
- 50% increase in the height of the result with 6 lines compared to the 4 of the rest of the search results.
Despite not being in first place for this search, the rich snippet result is getting 55% of the CTR according to Google Webmaster Tools, which means it is getting more visits than the first result.
Factors to consider when implementing structured data
- Choosing the structured data markup format: there are 3 ways to define structured data in our site:
- Microformats: this is the oldest and simplest data markup to implement. They are built with HTML element classes which implies that it mixes data markup with the definition of styles and this implies an important lack of extensibility.
- RDFa: this data markup adds attributes such as typeof or property to embed structured metadata in HTML tags. It is supported by the W3C and is more extensible than microformats. Initially Google did not support this data markup, but after repeated protests from industry professionals, it began to support it in its rich snippets.
- Microdata: this is the markup recommended by Google, HTML elements are marked up using itemscope, itemtype or itemprop attributes. It attempts to provide a simpler form of data markup than RDFa and microformats. The algorithm that processes it is much simpler than the one used to interpret RDFa, so data extraction is more reliable and easier to debug.
- Content markup: Google supports different types of data markup. We must select the type that best fits the data of our site.
- Opinions
- Persons
- Products
- Companies and organizations
- Recipes
- Events
- Music
- Test the implementation: Google offers us the possibility to test the implementation immediately and thus ensure that, when crawling the page again, the data markup is detected correctly. Once Google has crawled our site and detected our rich snippets we can check it in the Structured Data option in the Optimization section of Webmaster Tools.
Disadvantages of enriched fragments
But the use of rich snippets is not all advantages:
- If the elements displayed are not very accurate, it can reduce the CTR. For example, an image that is not very pleasing, or if we show a rating that is too low in the enriched fragment.
- By having all of our content stripped down, it is more understandable to automated tools and increases the ease with which our content can be scanned.
- It introduces a new form of SPAM as false content can be tagged in an attempt to boost CTR. Google offers a tool to report misuse of rich snippets.
What if we cannot implement rich formats?
There may be a situation where we cannot modify the necessary HTML of our site to be able to mark it up, in that case Google Webmaster Tools offers us the Data Marker to make Google learn the structure of the pages of our site.
We just have to follow a few simple steps:
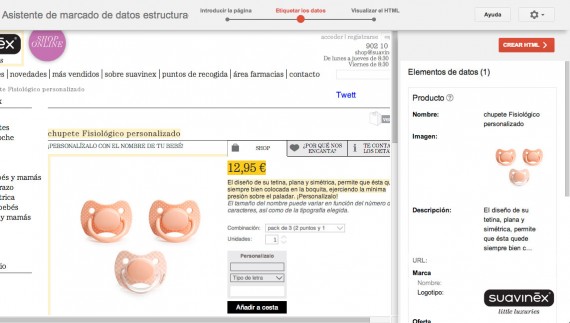
- Add the page to be “enriched”.
- Select the type of data accepted by Google, as you can see in the following screenshot, the types do not match those of the microdata.
- We can apply the data markup to the entered page or to all pages sharing the same template.
- Then an interface opens in which we select the parts corresponding to the data marking and identify it.
- Once confirmed, an entry will appear in the Data Marker.
- The markup will not be applied until the submitted page is crawled again.
- It also gives us the opportunity to undo the marking.
- A data marking wizard is also available for testing purposes.
We will use HTML markup if:
- We want to control the fields on each page
- We can add the necessary HTML to each page
- Site structure changes frequently
- Must be compatible with other search engines
We will use the data marker if:
- Our site displays data about events
- It is not possible to add HTML markup
- You do not have the knowledge to modify the templates
In addition to these recommendations that Google gives us to decide on one system or another, we must take into account:
- The data marker is only compatible with Google, it will not work with other search engines such as Bing.
- HTML markup always prevails over data markup, so if we already have the former implemented, there is no point in using Google Data Markup.
It is clear that if we do not appear on the first page of search results, rich snippets would not increase visits because most users would not see them. On the other hand, if we have done our SEO well and managed to appear among the first positions, rich snippets can increase our visibility compared to the competition and thus the visits to our site.