Written by Paolo Gorgazzi
Index
A good search engine optimization strategy starts with an analysis of the health of the website that allows to establish the appropriate steps to follow to achieve the objectives set at all times.
This diagnosis and subsequent analysis is called SEO Audit and is essential not only to know the progress achieved, but also to be aware of possible deviations that occur and that will lead to establish corrective measures.
The main objective of an SEO audit is to locate the crawling and content indexing barriers that prevent search engine robots from accessing your website and negatively influence the ranking of your products or services when a user performs a search related to them.
Any potential problems you encounter can be turned into opportunities for improvement that will set you apart from your competitors.
Structure of an SEO audit
At Human Level we know that there is no perfect structure for writing an SEO audit and this is the philosophy we apply to each of our clients. Each agency and each SEO professional implements their expertise to present the results of the audit according to their way of interpreting SEO and with the objective that the client understands the aspects to be improved on their site.
Analysis of each positioning factor
In an SEO audit, all aspects that influence the positioning of your website in search engine results are analyzed in depth. It is important to explain each step that the SEO consultant carries out so that as a client you know and understand the procedure performed in each analysis and at all times.
An example of how we present anSEO audit report at Human Level is as follows:
- Concept: short description of the factor being analyzed and its relation to SEO.
- Procedure: what tool we have used to carry out the check.
- Diagnosis: description of the problem encountered during the factor analysis.
- Recommendation: what actions need to be taken to turn the problem found into an opportunity for improvement.
Executive Report
At the beginning of the SEO audit white paper we consider it good practice to write an executive report in which non-technical language is used to explain the main problems/opportunities that have been found throughout the SEO audit for you to understand all the analysis that the SEO consultant has carried out.
Execution priorities
We know from experience that listing all of the problems/opportunities encountered without suggesting a order of priority how to attack them does not add value to the SEO audit, for this reason we usually accompany the executive report with a road map where we indicate which points will be worked on according to the expected results and, above all, the resources that will have to be invested in the corresponding actions.
Expected benefits
Finally, it is advisable to conclude the executive report by indicating and explaining the benefits we expect to obtain once we have implemented the optimizations proposed in the roadmap.
Annexes
The data collected during the different phases of the SEO audit and used to support and justify the suggested recommendations are collected in documents external to the audit report itself, e.g. Excel sheets or Google Sheets. We like to list the documents in the annexes section of the technical document to present them to you in a clear and orderly fashion.
What is analyzed in an SEO audit?
In an SEO audit, all aspects and factors of your website are analyzed in detail to detect those problems that prevent a correct positioning of your content, products and services in Google search results.
Almost all SEO audits agree on six major areas of analysis:
- Indexability audit
- Content
- Adaptation to Mobile-First indexing
- Implementation of international versions
- Download speed and user experience audit (WPO)
- Popularity
Let’s take a detailed look at each of them in order to explain the actions that are usually performed in an SEO audit.
Indexability
It is the accessibility that allows search engine robots to discover, crawl and finally index the content and then rank it when a user performs a search according to their intent.
In this phase of the SEO audit, technical barriers that prevent easy crawling by search engine bots are detected.
In Indexability, the key point is how robots see us. And, among other aspects, we reviewed the following.
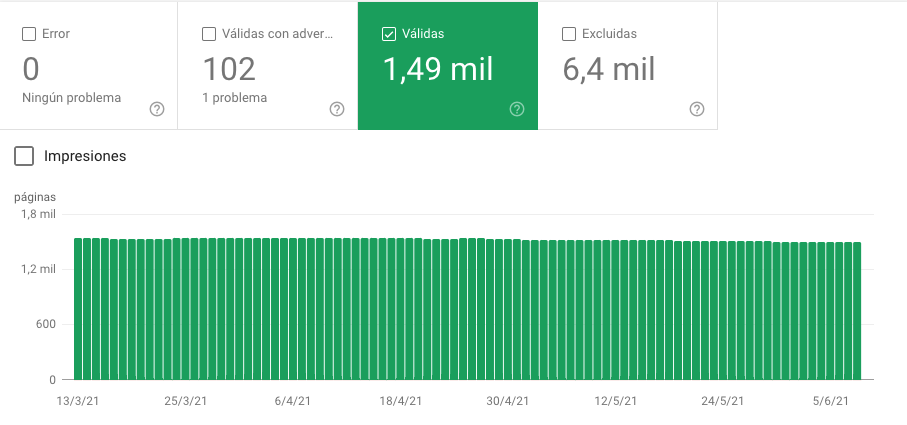
Pages indexed in Google
To determine the health of a website, it is essential to know its saturation index: the ratio between the total indexable pages of the site and the pages actually indexed by Google. Our goal will be to achieve 100%.
Sitemap file
It is a file that lists all the important URLs of a website. It is very beneficial in very large websites to take full advantage of the crawl-budget of the bots, the resources that search engines allocate to crawl our site. It must be exhaustive and updated.
Duplicate content
Content or blocks of content similar or equal to others that belong to our site or to other websites. Google bots do not like to read the same content more than once because they understand that we are not providing a differential value to the user.
Paginated contents
In an ecommerce we usually find paginated content in the product listings. It is a very delicate point and one that confronts many SEOs, since there are different ways of conceiving how to optimize them. They should facilitate the user experience as well as allow tracking of all pages of the site.
Canonical
It is a recommendation we make to Google bots when we have two or more pages with the same or similar content to indicate to search engines which of them is the main one. It is important to avoid indexing duplicate content. It is especially important when applying sorting filters on product listing pages, for example.
Meta robots
It is an HTML tag that allows us to control the indexing of a page, blocking the passage of Google bots when it is convenient for us.
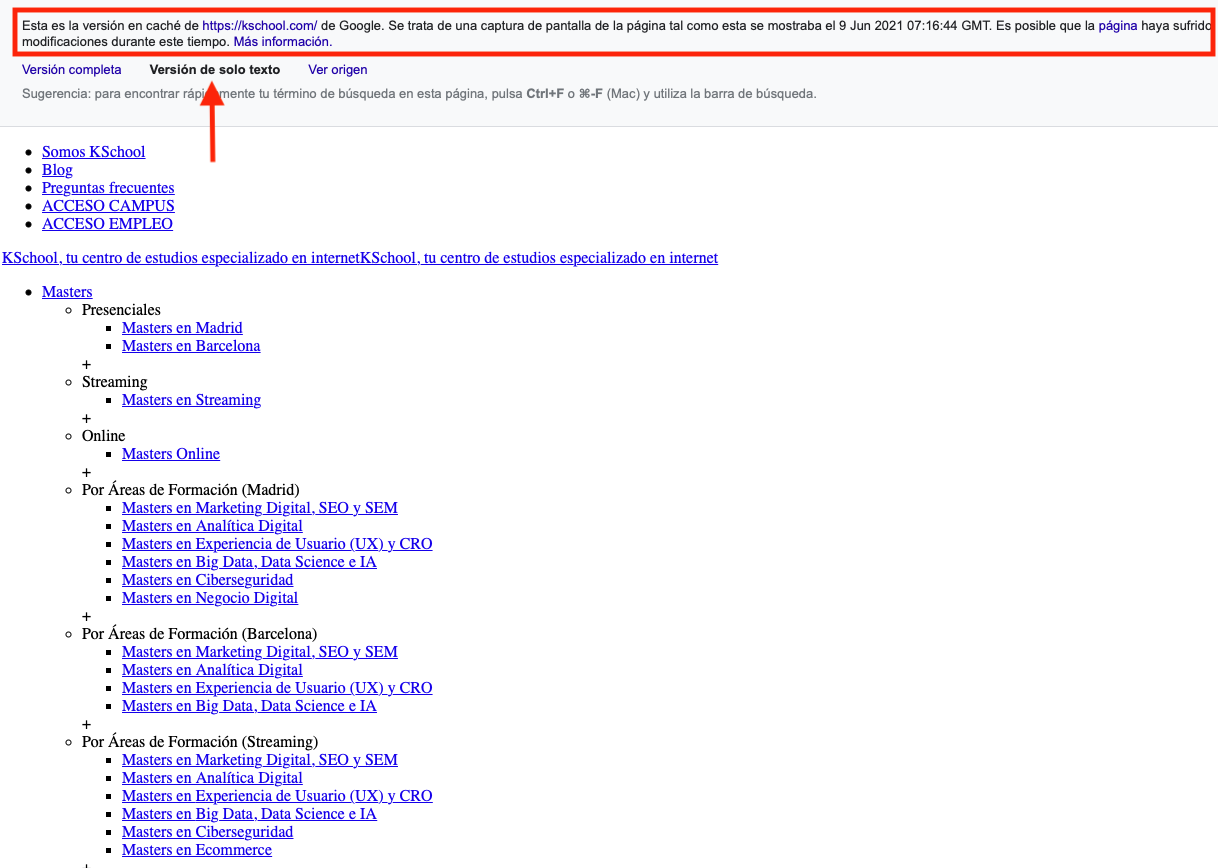
Google Cache
It is Google’s short-term memory where it stores the latest version of all pages accessible to its robot. Content, date, uncrawlable links and images without alternative text are some of the factors that can be analyzed by simply consulting the Google cache.
JavaScript disabled
The ever more diffuse use of JavaScript technology and its higher resource requirements impact the behavior of Google bots when crawling a website. Browsing a website by disabling JavaScript helps to uncover potential problems for its crawlability and indexing.
Page rendering
When a browser makes a request to a server to view the content of a page, the server responds with codes. The user, on the other hand, only has access to its graphical representation “painted” on his screen: what is technically called rendering.
robots.txt file
It is a simple text file where we can include instructions for Google bots to have access or not to certain sections of our website. Thanks to the robots.txt file we can modulate the crawling and indexing of certain content.
Nofollow links
It is an attribute that is given to one or more links on our website to stop link to stop the transfer of link juice from one from one page to another.
Search engine friendly URLs
The URLs of our website should be semantic and include the most important concepts of the page.
Content
Content plays a fundamental role in SEO as it is a relevant positioning factor for Google. Nowadays it is highly recommended to offer quality content to our users to satisfy their needs and search intentions and, consequently, to be able to be in the first positions in Google results.
Content is not just text: content is any image, video or program that can be accessed on the Internet through a web browser.
Titles in SERPs
Page titles are a relevant factor for SEO positioning. They must be unique, contain the keyword and meet the length criteria dictated by Google.
Snippet in SERPs
The meta-description is not a factor of relevance but it influences the CTR (click through rate), the number of clicks a link gets in relation to its number of impressions on search engine results pages (SERPs).
Hierarchy of Hn
The Hn titles are an SEO resource that provides an additional semantic layer to the content. If we correctly implement its hierarchy, the bots will better understand the content of our landing page in a way that positively influences the positioning of a certain content.
HTTP header analysis
HTTP response codes determine the status of the message sent by the server to the browser that requested a URL. These codes can be grouped into different categories. The following is a list of the most popular ones:
Satisfactory answers (2xx)
- 200 ok: the requested page was found successfully.
Redirections (3xx)
Redirections:
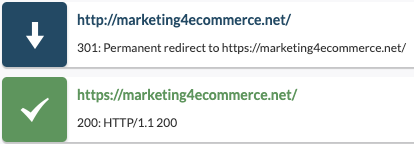
- 301 moved permanently: the requested page points to another URL permanently.
- 302 temporarily moved: the requested page points to another URL temporarily.
Customer errors (4xx)
Customer errors:
- Error 404: The requested page cannot be found.
- Error 410: The requested page has been deleted.
Server errors (5xx)
Server errors:
- Error 503: the server is unable to process the page request
IP blacklisting
If an IP address is “blacklisted” as a source of spam it can give the search engine a negative signal and could affect the website’s ranking.
IP Neighborhood
If the site shares a server with other domains, it is good practice to know who the potentially dangerous neighbors are, since this factor could sometimes affect the positioning, slowing down your download or causing frequent server crashes.
HTTP/HTTPS protocol
Websites must implement the SSL certificate so that the requests from the browser to the server and vice versa are encrypted and the information travels in a secure way, as protected as possible from computer attacks.
Mobile-first
Nowadays Google spiders crawl websites as if they were mobile, so the importance of having a site compatible with the different screen widths of the different devices on the market and with a fast download is fundamental.
Mobile-First: today mobile comes first
Mobile version
There are different ways to make our website compatible so that it can be viewed correctly on a smartphone. This is what mobile SEO is all about.
Responsive
A single HTML code and URL (presence of the viewport tag, only the CSS changes).
m.site
Two HTML codes and two different URLs (HTML markup: canonical tag from the mobile to the desktop version, alternate tag from the desktop to the mobile version, different CSS)
Dynamic
Two HTML codes and one URL (depending on the technology/device used to access the site: different user Agent tag, different CSS)
AMP
A copy of the website stored on Google servers (recommended for media only):
- HTML version: canonical tag to the page itself and amphtml link tag reference to AMP version
- AMP version: canonical to HTML version
International
If the site we are auditing targets users from different countries and languages or users of different languages living in the same country or users who speak the same language but live in different countries, we must verify the correct implementation of Google’s international SEO guidelines.
International SEO: do we meet Google’s standards?
Geographic orientation of the domain
In Google Search Console we have the possibility of configuring a geographic orientation for our domain, subdomain or subdirectory.
Use of CDN
The CDN (Content Delivery Networks) are mirror servers present in different territories around the world whose function is to accelerate download speed. They are often used when the website’s audiences are located in different countries around the world. This spreads the load among different servers and reduces latency by being closer to your users.
Label hreflang
It is an HTML attribute to specify the language and geographic target of a web page. If there are different language versions of a website, we must verify the correct implementation of this attribute.
WPO
WPO stands for Web Performance Optimization.
The WPO is in charge of optimizing a website so that it loads as fast as possible according to the parameters of the search engines.
Using HTTPS with HTTP/2 or HTTP/3
The HTTP/2 and now HTTP/3 protocols together with HTTPS make it possible to speed up web downloading compared to the use of the HTTP 1.1 protocol.
HTML code download time
It is the sum of two metrics:
- TTFB (Time to first byte): the time it takes for the server to start sending the page to the browser.
- Download time: the total download time of the HTML.
Total loading time
It is the time it takes for the page to be completely loaded in the browser, it is called DOM (Document Object Model) loaded.
DNS resolution time
The DNS (Domain Name System) resolution time affects the time it takes for the server to receive and process a request for a web page, known as latency.
Connection time
Time spent by the browser to establish a connection with the server.
Page file size
The page size affects the indexing of a website since Google grants a limited time to the crawl of each site (crawl budget).
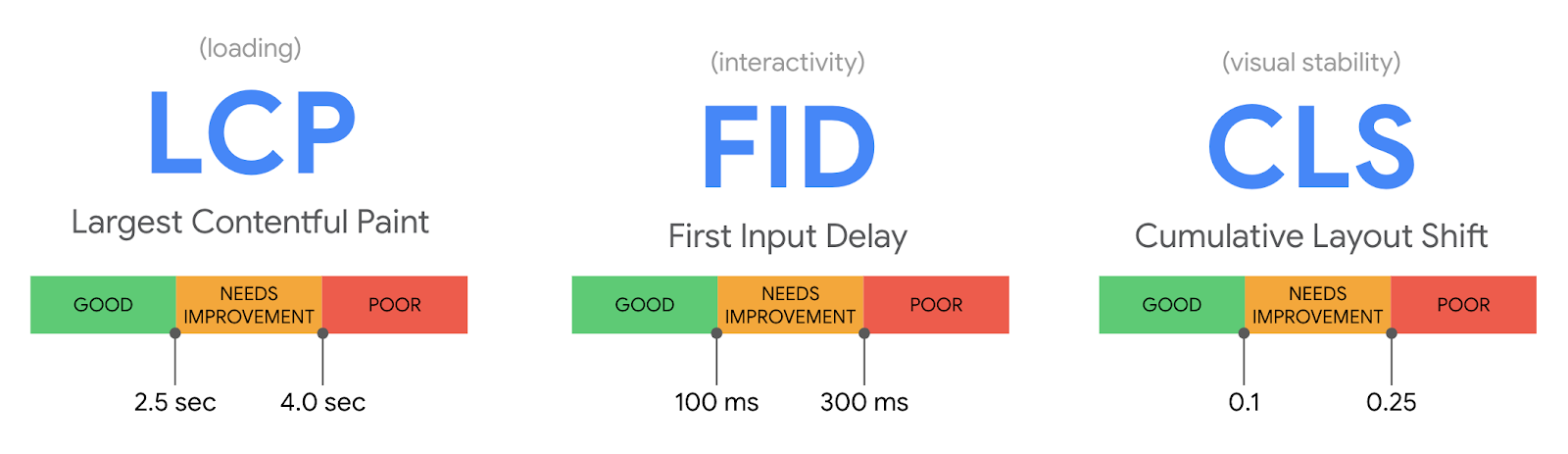
Core Web Vitals: user-oriented metrics
The so-called user-oriented metrics are already a relevant factor for Google. We can briefly summarize these metrics as follows:
- FID (First Input Delay): time that elapses from the moment a user clicks on an element of our website until the browser responds (an optimal result for Google is less than 100 ms).
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): time taken to render the largest above-the-fold element on the page (an optimal result for Google is less than 2.5 sec)
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): measures the visual stability of elements within a page (an optimal result for Google is less than 0.1).
JavaScript and CSS in external files
JavaScript and CSS resources are often located on external servers in relation to where our domain is hosted. We will check that none of these resources is blocked by a robots.txt file out of our control.
Popularity
It is related to the number of inbound links pointing to our site from other websites.
Search engines do not give the same value to all links as some have more weight than others depending on the quality of the source domain.
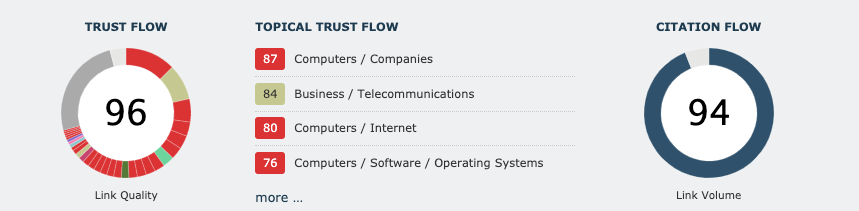
External inbound links and suspicious domains
The quantity and quality of inbound links (backlinks) can be measured thanks to two metrics provided by the Majestic tool:
- Trust Flow: score of a domain after checking the quantity and quality of links.
- Citation Flow: counting of the number of links or mentions to our site
Conclusions
The SEO audit of a website is an exhaustive and meticulous analysis process where the experience of the consultant who carries it out is fundamental to locate the weak points of the site. Likewise, the experience of the SEO consultant is very important to know how to turn the weaknesses found into opportunities for improvement.
Human Level is an SEO agency with more than 22 years of experience, we have worked with hundreds of national and international companies obtaining important results in the positioning of content in search engines, especially in Google. Our clients are large and medium-sized companies from multiple business sectors: media, eCommerce, technology companies and many others that trust us and our work methodology as a guarantee of results.